How information about new medicines gets into the NHS
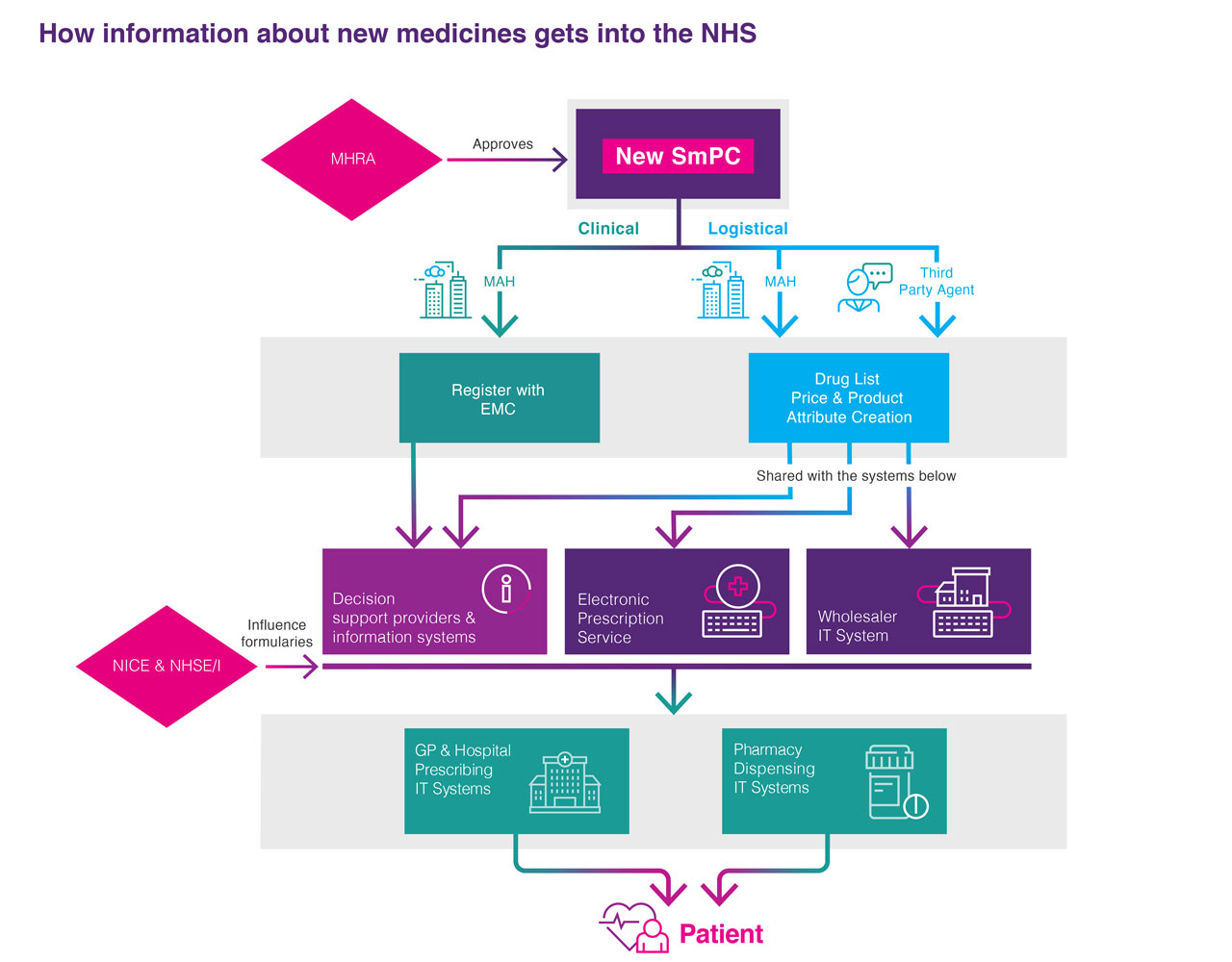
When a new medicine is licensed by the MHRA, a series of information flows need to be set in train so that essential information about the new medicine is set up on a range of information systems in a timely manner.
This allows prescribers and dispensers of the medicine to place orders so that the medicine can be given to patients when they need it. The information includes clinical, logistical, administrative and pricing data items. Additional information about where the medicine should be used within a treatment pathway, and guidance about which patients can be given the medicine on the NHS, is also added into hospital and GP clinical decision support and pharmacy IT systems.
ABPI has created a bitesize infographic to show how this information flows through the system.
Further information
Clinical
Reflects the steps a MAH must follow to make the new medicine’s information (Summary of Products Characteristics and Patient Information Leaflet) available to prescribers and dispensers.
- Electronic Medicines Compendium: Provides up to date, approved and regulated prescribing and patient information for licensed medicines (EMC).
- Decision support providers & information systems: Examples of these would be the BNF, the Monthly Index of Medical Specialities (MIMS), EMIS, and other IT Prescribing/dispensing systems. They assist Health Care Professionals to make informed decisions about what are the best medicinal treatments for patients.
Glossary
- MAH: Marketing Authorisation Holder.
- MHRA: The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency.
- NHSE/I: NHS England and Improvement.
- NICE: The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence.
- SmPC: Summary of Product Characteristics.
Logistical
Reflects the steps a MAH must follow to make the new medicine physically available at a pharmacy so a prescriber can order it.
- Third party agent: An organisation that works on behalf of or independently of the MAH to help support the creation of all the product attributes to ensure the product is available to order. For example they could set a new medicine up by contacting all the available organisations (e.g. Dictionary of medicines and devices (dm+d), British National Formulary (BNF), Chemist & Druggist (C+D), etc) that need to be notified when a new product is launched. An example of third party agent would be EMC Supply Chain.
- Drug List Price & Product Attribute Creation: The approved price and various product codes are set up to support the efficient ordering and distribution of medicines through the supply chain.
- Wholesaler IT System: Once a medicine is set up within the Wholesaler IT systems it can be ordered by a Health Care Professional (prescriber first and then a dispenser). This means it can be distributed from a warehouse and ultimately to the patient.
- Electronic Prescription Services (EPS): This service allows the medicine to be ordered by a prescriber and dispensed in the pharmacy. It is fully functioning in primary care and is expanding to secondary care. Find out more about the EPS.
Related content in this section:
Last modified: 12 November 2024
Last reviewed: 12 November 2024
